QUICK APPOINTMENT FORM

What is Uveitis?
Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea layer, which forms the middle layer of the eye. The uvea consists of the iris, ciliary body and choroid. This inflammation in particular can cause various symptoms such as eye pain, redness, blurred vision and sensitivity to light.
Uveitis is a serious condition that can lead to permanent vision loss and therefore early diagnosis and treatment is very important.
What are the Types of Uveitis?
The uvea is a layer that includes the iris, ciliary body and choroid and is responsible for the blood flow and nutrition of the eye. Although uveitis is not a disease in itself, it can be a complication of many different diseases and infections.
Uveitis is divided into three main categories according to the area of the uvea where the inflammation occurs. Anterior Uveitis (Iritis or Iridocyclitis) is inflammation of the iris and ciliary body in the front part of the eye. Anterior uveitis is the most common type of uveitis.
It usually causes symptoms such as sudden onset, severe pain, redness, sensitivity to light and blurred vision. Intermediate Uveitis (Intermediate Uveitis) is an inflammation of the ciliary body and choroid at the back of the eye.
It is less common than anterior uveitis and usually causes less pronounced symptoms. Blurred vision, floaters and night blindness are among the most common symptoms. Posterior uveitis is inflammation of the choroid and retina at the very back of the eye.
It is the least common type of uveitis and carries the most serious risk of complications. It can cause symptoms such as blurred vision, pain, flying objects and narrowing of the visual field. Other types of uveitis are as follows.
- Panuveitis is an inflammation that affects all uveal layers of the eye.
- Granulomatous Uveitis is a type of uveitis that occurs due to infections and causes small nodules to form in the eye.
- Masquerade Uveitis is a type of uveitis that masks the symptoms of another underlying disease.
What are the Symptoms of Uveitis?
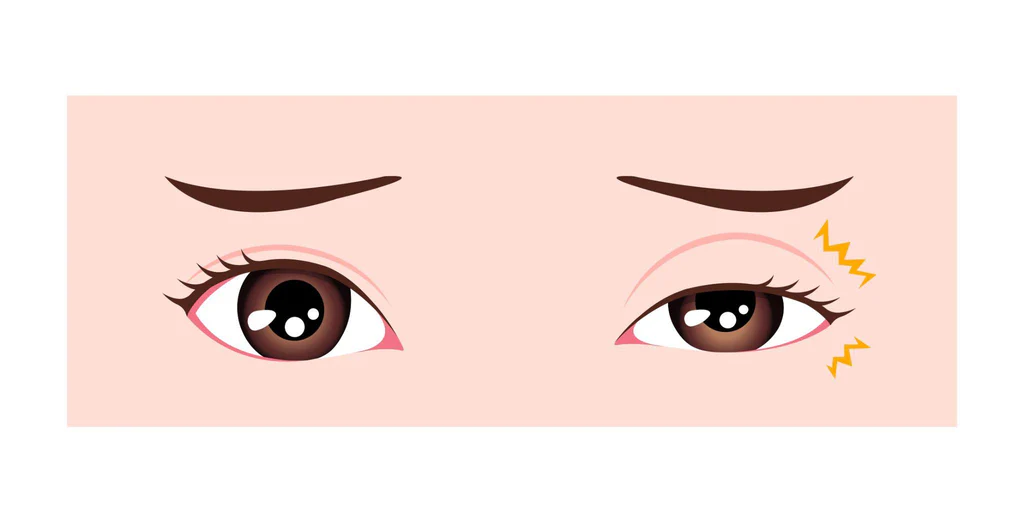
Uveitis, an inflammatory condition affecting the middle layer of the eye (uvea), can manifest itself with many different symptoms. The most common uveitis symptoms are as follows.
- Eye pain is the most common symptom of uveitis. The pain may be sharp or aching and may be affected by light.
- Redness may be seen in the white part of the eye or iris.
- Hypersensitivity to light and glare are common symptoms of uveitis.
- Blurred vision may be mild or severe and may occur in one or both eyes.
- Black dots or spots floating in front of the eyes may appear.
- Excessive watering of the eyes may be a symptom of uveitis.
- Eyelid drooping can be seen in the eye with uveitis.
What Causes Uveitis?
Although the cause of more than 50% of uveitis cases is unknown, infections, autoimmune diseases and traumas are among the most common causes. The causative agents of uveitis include the following.
- Viruses (herpes, toxoplasma), bacteria (tuberculosis, syphilis), fungi and parasites are microorganisms that can cause uveitis.
- Diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, Behçet’s disease, ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis, in which the immune system attacks healthy tissues, can also cause uveitis.
- Impacts and punctures to the eye area can cause uveitis.
- Some systemic diseases such as saroidosis, vasculitis and multiple sclerosis may also contribute to uveitis.
- Uveitis can also occur after eye surgeries such as cataract and glaucoma.
- Some medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs and some antibiotics can cause or trigger uveitis.
- It is seen that some families are more predisposed to uveitis.
Uveitis Diagnosis and Treatment
Uveitis is diagnosed with a comprehensive eye examination by an ophthalmologist. Your doctor will use a slit lamp to examine your eyes. He or she may also order blood tests and imaging tests to determine the cause of uveitis.
The diagnosis of uveitis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the disease. Mild cases of uveitis can be treated with steroid drops or ointments. More severe cases may require stronger medications such as oral steroids, immunosuppressants or biological agents.
Uveitis caused by infection is treated with antibiotics, antivirals or antifungal drugs.
How Much Is Uveitis Treatment Price?
Uveitis treatment price varies depending on the underlying cause and the operation to be performed. The treatment plan to be created by our specialist ophthalmologist depending on the detailed examination results may vary from person to person.
Please click here for appointment and price information.
The above information is for informational purposes. If you have any medical concerns or questions, please make an appointment with our ophthalmologists.